At Sarvotham’s we have observed tight belt put extra pressure on your digestive system and so it disturbs the normal flow of digestion…Tight belt will also cause the acid to go back upward and will cause acid re-flux and heartburn. Due to the extra pressure on gut, it will also cause stomach discomfort and stomach. Our observation is that increased pressure in the abdomen can cause stiffness in the spine and stress on the back. If the belt is too tight and low riding, it causes nerve compression in the back.
Recommendations for keeping one’s back healthy
Following any period of prolonged inactivity, a regimen of low-impact exercises is advised. Speed walking, swimming, or stationary bike riding 30 minutes daily can increase muscle strength and flexibility. Yoga also can help stretch and strengthen muscles and improve posture. Consult a physical instructor for a list of low-impact, age-appropriate exercises that are specifically targeted to strengthening lower back and abdominal muscles.
Always stretch before exercise or other strenuous physical activity.
Don’t slouch when standing or sitting. The lower back can support a person’s weight most easily when the curvature is reduced. When standing, keep your weight balanced on your feet.
At home or work, make sure work surfaces are at a comfortable height.
Sit in a chair with good lumbar support and proper position and height for the task. Keep shoulders back. Switch sitting positions often and periodically walk around the office or gently stretch muscles to relieve tension. A pillow or rolled-up towel placed behind the small of the back can provide some lumbar support. During prolonged periods of sitting, elevate feet on a low stool or a stack of books.
Wear comfortable, low-heeled shoes.
Sleeping comfortable as desired with the knees drawn up in a fetal position can help open up the joints in the spine and relieve pressure by reducing the curvature of the spine. Always sleep on a medium firm mattress.
Don’t try to lift objects that are too heavy. Lift from the knees, pull the stomach muscles in, and keep the head down and in line with a straight back. When lifting, keep objects close to the body. Do not twist when lifting.
Maintain proper nutrition and diet to reduce and prevent excessive weight gain
Three most common cause of Back Pain.
Sprains and strains account for most acute back pain. Sprains are caused by overstretching or tearing ligaments, and strains are tears in tendon or muscle. Both can occur from twisting or lifting something improperly, lifting something too heavy, or overstretching. Such movements may also trigger spasms in back muscles, which can also be painful.
Intervertebral disc degeneration is one of the most common mechanical causes of low back pain, and it occurs when the usually rubbery discs lose integrity as a normal process of aging. In a healthy back, intervertebral discs provide height and allow bending, flexion, and torsion of the lower back. As the discs deteriorate, they lose their cushioning ability.
Herniated or ruptured discs can occur when the intervertebral discs become compressed and bulge outward (herniation) or rupture, causing low back pain.
Outfit And Pain
Specifically, outfits that are too tight, too stiff, or too constricting can limit your range of motion, which causes more stress and strain to fall on your back, neck, and shoulders, increasing your risk of pain and injury. … Another common culprit for back and neck pain could be your sports bra. Any clothing or shoes that change your range of motion or your body’s shape (think tight, stiff or constricting) can harm your spine because they strain your back, neck, and shoulders.
Radiculopathy
A condition caused by compression, inflammation and/or injury to a spinal nerve root. Pressure on the nerve root results in pain, numbness, or a tingling sensation that travels or radiates to other areas of the body that are served by that nerve. Radiculopathy may occur when spinal stenosis or a herniated or ruptured disc compresses the nerve root.
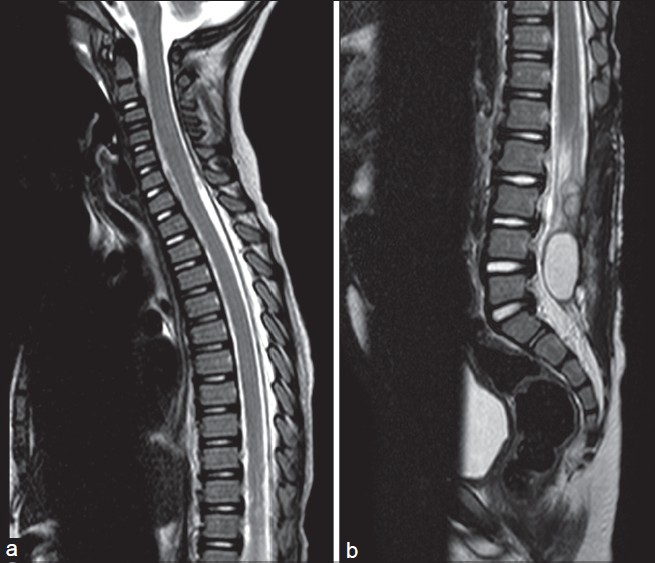
What is MRI? (Magnetic resonance imaging)
A magnetic force instead of radiation to create a computer-generated image. Unlike x-ray, which shows only bony structures, MRI scans also produce images of soft tissues such as muscles, ligaments, tendons, and blood vessels. An MRI may be ordered if a problem such as infection, tumor, inflammation, disc herniation or rupture, or pressure on a nerve is suspected. MRI is a non-invasive way to identify a condition requiring prompt surgical treatment. However, in most instances, unless there are “red flags” in the history or physical exam, an MRI scan is not necessary during the early phases of low back pain.
What is X-ray
Its often the first imaging technique used to look for broken bones or an injured vertebra. X-rays show the bony structures and any vertebral misalignment or fractures.
Soft tissues such as muscles, ligaments, or bulging discs are not visible on conventional x-rays.
The Lower Back
Lower back is a complex spot, with many potential sources of pain. Although surgery would seem to be a quick fix, in reality about 85% of people don’t need—and won’t benefit from—back surgery, says Anders Cohen, MD, chief of neurosurgery at the Brooklyn Hospital Center, in New York City. Sarvotham’s therapy specializes treating such back ailments without surgery
Occipital Neuralgia
Occipital neuralgia is the term for a headache that starts in the upper neck or back of the head and spreads or radiates behind the eyes, forehead, and up to the scalp.
How Is Low Back Pain Diagnosed?
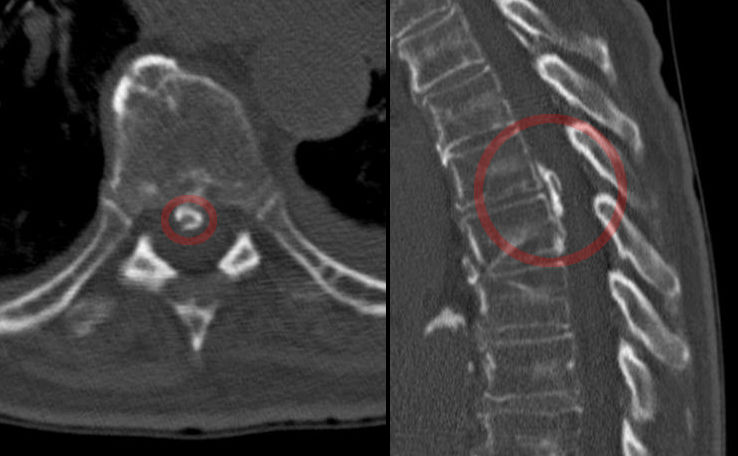
Imaging tests are not warranted in most cases. Under certain circumstances, however, imaging may be ordered to rule out specific causes of pain, including tumors and spinal stenosis. Imaging and other types of tests include:
X-ray is often the first imaging technique used to look for broken bones or an injured vertebra. X-rays show the bony structures and any vertebral misalignment or fractures. Soft tissues such as muscles, ligaments, or bulging discs are not visible on conventional x-rays.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a magnetic force instead of radiation to create a computer-generated image. Unlike x-ray, which shows only bony structures, MRI scans also produce images of soft tissues such as muscles, ligaments, tendons, and blood vessels. An MRI may be ordered if a problem such as infection, tumor, inflammation, disc herniation or rupture, or pressure on a nerve is suspected. MRI is a non-invasive way to identify a condition requiring prompt surgical treatment. However, in most instances, unless there are “red flags” in the history or physical exam, an MRI scan is not necessary during the early phases of low back pain.
Blood tests are not routinely used to diagnose the cause of back pain; however, in some cases, they may be ordered to look for indications of inflammation, infection, and/or the presence of arthritis. Potential tests include complete blood count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and C-reactive protein. Blood tests may also detect HLA-B27, a genetic marker in the blood that is more common in people with ankylosing spondylitis or reactive arthritis (a form of arthritis that occurs following infection in another part of the body, usually the genitourinary tract).
Recommendations for keeping one’s back healthy Low-impact exercises is advised. Walking, swimming, or stationary bike riding 30 minutes daily can increase muscle strength and flexibility. Yoga can also help stretch and strengthen muscles and improve posture. Make a list of low-impact, age-appropriate exercises that are specifically targeted to strengthening lower back and abdominal muscles. Always stretch before exercise
Don’t slouch when standing or sitting. The lower back can support a person’s weight most easily when curvature is reduced. When standing, keep your weight balanced on your feet.
At home or work, make sure work surfaces are at a comfortable height.Chair with good lumbar support. Switch sitting positions often and periodically walk around the office or gently stretch muscles to relieve tension. A pillow or rolled-up towel placed behind the small of the back can provide some lumbar support. During prolonged periods of sitting, elevate feet on a low stool or a stack of books. Sleeping comfort as desired in a fetal position can help open up the joints in the spine and relieve pressure by reducing the curvature of the spine. Always sleep on a medium firm mattress. Don’t try to lift objects that are too heavy. Lift from the knees, pull the stomach muscles in, and keep the head down and in line with a straight back. When lifting, keep objects close to the body. Do not twist when lifting. Maintain proper nutrition and diet to reduce and prevent excessive weight gain